Welcome to The Coding College, your reliable source for Python programming knowledge! In this post, we’ll explore the Python math module, a powerful library for performing mathematical operations. If you work with numbers, calculations, or scientific applications, the math module is a must-know tool.
What is the Python math Module?
The math module is a built-in Python library that provides a wide range of mathematical functions and constants. It simplifies performing advanced calculations without manually implementing formulas.
Importing the math Module
To use the math module, import it into your program:
import math Commonly Used Functions in the math Module
Here are some of the most useful functions provided by the math module:
1. Rounding Functions
math.ceil(x)
Returns the smallest integer greater than or equal to x.
import math
print(math.ceil(4.3)) # Output: 5 math.floor(x)
Returns the largest integer less than or equal to x.
print(math.floor(4.7)) # Output: 4 2. Power and Logarithmic Functions
math.pow(x, y)
Returns x raised to the power of y.
print(math.pow(2, 3)) # Output: 8.0 math.sqrt(x)
Returns the square root of x.
print(math.sqrt(16)) # Output: 4.0 math.log(x, base)
Returns the logarithm of x to the given base.
print(math.log(100, 10)) # Output: 2.0 3. Trigonometric Functions
The math module includes several trigonometric functions that work with angles in radians.
Convert Degrees to Radians and Vice Versa
print(math.radians(180)) # Output: 3.141592653589793
print(math.degrees(math.pi)) # Output: 180.0 Common Trigonometric Functions
print(math.sin(math.pi / 2)) # Output: 1.0
print(math.cos(0)) # Output: 1.0
print(math.tan(math.pi / 4)) # Output: 1.0 4. Constants
math.pi
The mathematical constant π (pi), approximately 3.14159.
print(math.pi) # Output: 3.141592653589793 math.e
The mathematical constant e (Euler’s number), approximately 2.71828.
print(math.e) # Output: 2.718281828459045 5. Factorial and Combinatorics
math.factorial(x)
Returns the factorial of x (non-negative integer).
print(math.factorial(5)) # Output: 120 math.comb(n, k)
Returns the number of ways to choose k items from n items without repetition.
print(math.comb(5, 2)) # Output: 10 6. Working with Floating Point Numbers
math.isclose(a, b, rel_tol=1e-9)
Checks if two floating-point numbers are close to each other.
print(math.isclose(0.1 + 0.2, 0.3)) # Output: True math.fabs(x)
Returns the absolute value of x.
print(math.fabs(-4.5)) # Output: 4.5 Example: Calculate the Area of a Circle
import math
radius = 5
area = math.pi * math.pow(radius, 2)
print(f"The area of the circle is {area:.2f}") Output: The area of the circle is 78.54
Exercises to Practice Python Math
Exercise 1: Calculate Compound Interest
Write a program to calculate compound interest using the formula:
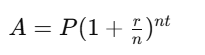
Exercise 2: Find the Hypotenuse
Using the Pythagorean theorem, calculate the hypotenuse of a right triangle given the lengths of the other two sides.
Exercise 3: Degree-Radian Converter
Create a program to convert an angle from degrees to radians and vice versa.
Why Learn Python Math with The Coding College?
At The Coding College, we focus on hands-on learning and real-world applications. By mastering the math module, you’ll unlock new capabilities in scientific computing, data analysis, and algorithm development.
Conclusion
The Python math module is a treasure trove for developers working with numbers. From simple arithmetic to advanced computations, it provides tools to streamline your workflow and solve complex problems efficiently.